Flutter Flow: Custom Marker Map (Place Manager)
Published on January 11, 2025
Flutter Flow: Place Manager(Library Migration, MapBox SDK, flutter_map)
Recently custom code templates were migrated to libraries.
Note: I have also now included polygons and polylines in this library for the tile and Google map.

There were a few issues I noticed in the migration. The CustomDataTypeMap file was kept, but the Mapbox widgets params were used instead. Also the custom data type **place **is also missing when adding it to a project. This caused errors if you add it to your project.
I have fixed these issues and there are now new updates
Map Library Updates
I have also included a new map widget Tile Map based on flutter_map. You can use this similarly to the Map Box article I posted. The benefits of flutter_map is that it includes built in functionality that the Map Box SDK doesn’t currently have. I will dive deeper into the tile map in a separate article.
Setting Up Google Maps on Flutter Flow
To get started follow the Flutter Flow Google Maps instructions : Generate Maps Keys | FlutterFlow Documentation
Add the Flutter Flow Google Map widget to a blank page
To complete the set up you will need to include a Flutter Flow Google Map widget on a blank page. This is a work around that sets up the the keys for you when you download and/or publish the app.
You can follow Flutter Flow official instructions to understand how to do this: Google Maps Widget | FlutterFlow Documentation
Automate the set up process
It can be tedious to manually set this up. This is optional but handles a lot of the steps discussed in the rest of this article
You can automate most of this process at https://codewhims.com/ and choosing the Place Manager option

From there you can define custom columns for place, polygon, and polyline data

You can also connect to your Supabase project. From here you can automatically create tables without needing to manually input the data.

We also still give the schema for you to copy in case you want to manually add the data. Benefit of this, is that it matches the schema you defined above.

Later in this article we discuss mapping your data to the custom map data. We also automatically update this code based on the columns you define above.
There is also another separate dashboard that will help you add data seamlessly for places, custom markers, polygons, polylines, etc. You will be able to purchase once and use across multiple projects. We will also handle deploying this online so there is zero setup on your side.
This part is not yet released but will be soon!

Follow along below if you to manually set up the custom map widgets.
Setting up the database
You can set your location table on Supabase and Firebase to have any column you desire.
The following is for Supabase but I will include instructions for Firebase soon. You can set up your Firebase Collections with a similar structure.
If you don’t have tables you can start with these on Supabase.


You can also run this in the SQL Editor on Supabase.

Create the place table.
CREATE TABLE public.place (
id bigint generated by default as identity not null,
created_at timestamp with time zone not null default now(),
title text null,
description text null,
latitude double precision null,
longitude double precision null,
image_url text null,
constraint place_pkey primary key (id)
) TABLESPACE pg_default;
Make sure to turn on RLS and set up your RLS policies before releasing to production to keep your data secure. This policy allows us any user to read from the table.
-- Enable RLS on the place table
ALTER TABLE place ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
-- Allow authenticated users to read all templates
CREATE POLICY "Allow users to read places"
ON place FOR SELECT
USING (true);
Now for polygons we have two tables. For each polygon we save to the polygon table. This will hold important overall data about the polygon such as colors and stroke weights.
create table public.polygon (
id serial not null,
title text null,
description text null,
fill_color text null,
fill_opacity numeric null,
stroke_color text null,
stroke_opacity numeric null,
stroke_weight numeric null,
created_at timestamp with time zone not null default now(),
zoom numeric null default 10,
constraint polygon_pkey primary key (id),
) TABLESPACE pg_default;
create table public.polygon_place (
id serial not null,
polygon_id integer null,
name text null,
title text null,
description text null,
address text null,
city text null,
state text null,
zip_code text null,
latitude numeric null,
longitude numeric null,
image_url text null,
"order" integer null,
created_at timestamp with time zone not null default now(),
constraint polygon_place_pkey primary key (id),
constraint polygon_place_polygon_id_fkey foreign KEY (polygon_id) references polygon(id) on delete CASCADE
) TABLESPACE pg_default;
-- Enable RLS on the tables
ALTER TABLE polygon ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
ALTER TABLE polygon_place ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
-- Allow authenticated users to read all templates
CREATE POLICY "Allow users to read polygons"
ON polygon FOR SELECT
USING (true);
CREATE POLICY "Allow users to read polygon places"
ON polygon_place FOR SELECT
USING (true);
Similarly polylines have two tables for the same reason as polygon
create table public.polyline (
id serial not null,
title text null,
description text null,
stroke_color text null,
stroke_opacity numeric null,
stroke_weight numeric null,
geodesic boolean null,
created_at timestamp with time zone not null default now(),
zoom numeric null default 10,
constraint polyline_pkey primary key (id),
) TABLESPACE pg_default;
create table public.polyline_place (
id serial not null,
polyline_id integer null,
title text null,
description text null,
address text null,
city text null,
state text null,
zip_code text null,
latitude numeric null,
longitude numeric null,
image_url text null,
"order" integer null,
created_at timestamp with time zone not null default now(),
constraint polyline_place_pkey primary key (id),
constraint polyline_place_polyline_id_fkey foreign KEY (polyline_id) references polyline (id) on delete CASCADE
) TABLESPACE pg_default;
-- Enable RLS on the tables
ALTER TABLE polyline ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
ALTER TABLE polyline_place ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
-- Allow authenticated users to read all templates
CREATE POLICY "Allow users to read polylines"
ON polyline FOR SELECT
USING (true);
CREATE POLICY "Allow users to read polyline places"
ON polyline_place FOR SELECT
USING (true);
Adding the library to your project
To add the library to your project click on Settings > Project Dependencies
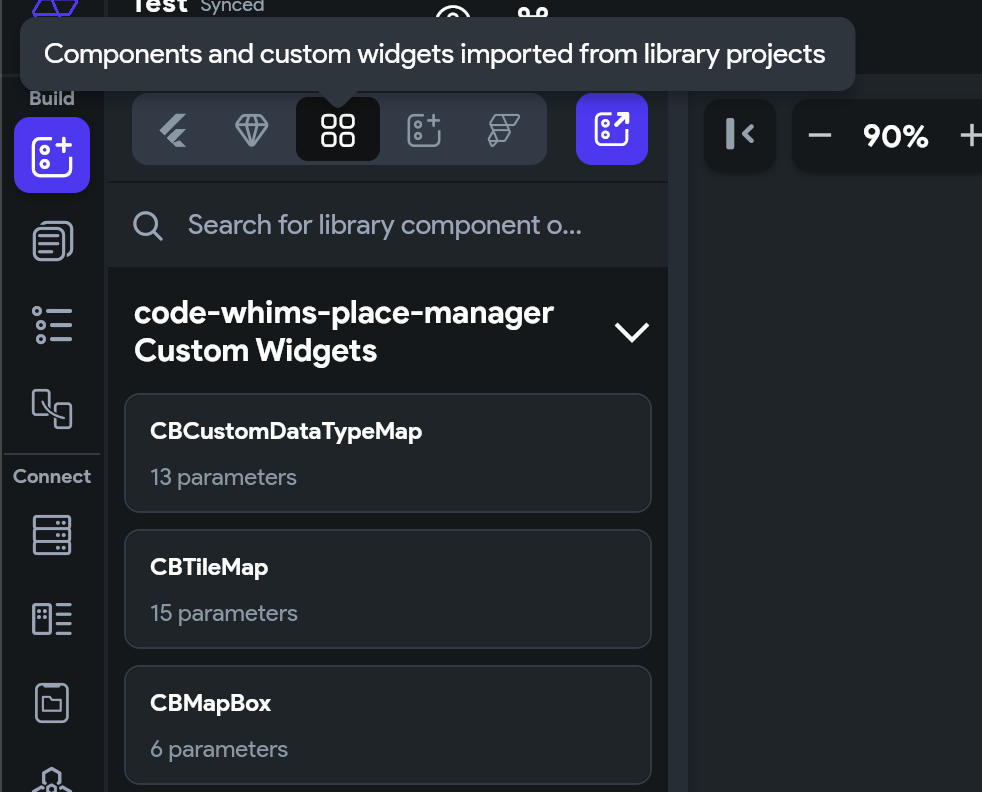
Next, choose the code-whims-place-manager library.

You will notice it shows the name as supabase-google-map-library when you download the code . This is the initial name of the project I created when developing the template, which is unable to be changed. Just an FYI.
Adding the custom maps to your Flutter Flow pages
To add the custom maps to your page choose the first icon under the Build menu to the far left of Flutter Flow, the Widget Pallete. Then choose the icon with four squares. Drag the widget you want on the screen.
Next click on the Widget Tree menu item (3rd item under the Build menu)

From here we can start adding our local state.
On the far right of Flutter Flow, click the State Management tab.

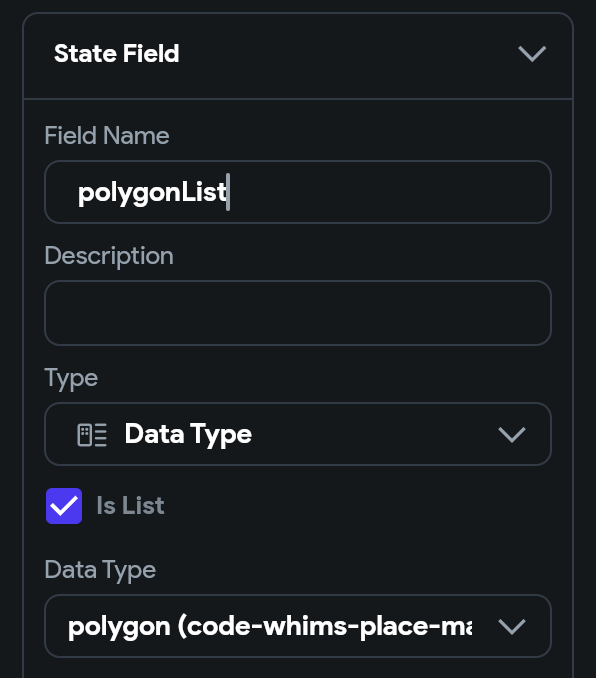
You can see that I have a placeList local page state variable. It’s a list of data types for the libraries place data type.
If you want to use polygons and polylines you will need to create similar local page state variables.
Polygon local page state variable:
Polyline local page state variable:

Custom Functions
Before querying from the database, you will need to map your data from your backend service to the data types used by the map widgets. To do this you will need to add custom functions to your Flutter Flow project. These are not a requirement so fill free to exclude what you do not need.
Below are functions for places, polygons, and polylines for Supabase. Mapping functions for Firebase are similar and will be added soon.
If you are new to custom functions in Flutter Flow, check out their documentation: https://docs.flutterflow.io/concepts/custom-code/custom-functions/
Supabase Polylines mapping function
First let’s start with Polylines. You can choose any name but make sure to change in the code as well. Here I use toPolylinePlaceModel

Next we need to define the return type. Choose Data Type and check the Is List and Nullable options. Choose the polyline (code-whims-place-manager) data type.

For the arguments we are passing a list of rows from tables polyline_place and polyline. We need to do this so we can map the points for each polyline.

Replace the default code with the code below
import 'dart:convert';
import 'dart:math' as math;
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:google_fonts/google_fonts.dart';
import 'package:intl/intl.dart';
import 'package:timeago/timeago.dart' as timeago;
import '/flutter_flow/custom_functions.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/lat_lng.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/place.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/uploaded_file.dart';
import '/backend/schema/structs/index.dart';
import '/backend/supabase/supabase.dart';
import "package:supabase_google_map_library_s065pd/backend/schema/structs/index.dart"
as supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema;
List<supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema.PolylineStruct>?
toPolylinePlaceModel(
List<PolylinePlaceRow>? supabasePolylinePlaces,
List<PolylineRow>? supabasePolylines,
) {
/// MODIFY CODE ONLY BELOW THIS LINE
// Map Supabase polyline list to library polyline list
return supabasePolylines?.map((polyline) {
// Get places for this polyline
final polylinePlaces = supabasePolylinePlaces
?.where((place) => place.polylineId == polyline.id)
.map((place) {
return supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema
.createPolylinePlaceStruct(
id: place.id,
title: place.title,
coordinates:
LatLng(place.latitude ?? 0.0, place.longitude ?? 0.0),
polylineId: place.polylineId,
order: place.order,
);
}).toList() ??
[];
return supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema.PolylineStruct(
id: polyline.id,
title: polyline.title,
zoom: polyline.zoom ?? 11,
strokeWeight: polyline.strokeWeight ?? 1,
strokeColor: polyline.strokeColor,
strokeOpacity: polyline.strokeOpacity,
geodesic: polyline.geodesic,
polylinePlaces: polylinePlaces,
);
}).toList() ??
[];
/// MODIFY CODE ONLY ABOVE THIS LINE
}
Supabase Polygon mapping function
For polygons I use the name toPolygonPlaceModel.

The return type and arguments are similar to polylines but use the polygon (code-whims-place-manager) data type instead.

For the arguments we are passing a list of rows from tables polygon_place and polygon. We need to do this so we can map the points for each polyline.

Replace the default code with the code below
import 'dart:convert';
import 'dart:math' as math;
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:google_fonts/google_fonts.dart';
import 'package:intl/intl.dart';
import 'package:timeago/timeago.dart' as timeago;
import '/flutter_flow/custom_functions.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/lat_lng.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/place.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/uploaded_file.dart';
import '/backend/schema/structs/index.dart';
import '/backend/supabase/supabase.dart';
import "package:supabase_google_map_library_s065pd/backend/schema/structs/index.dart"
as supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema;
List<supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema.PolygonStruct>?
toPolygonPlaceModel(
List<PolygonPlaceRow>? supabasePolygonPlaces,
List<PolygonRow>? supabasePolygons,
) {
/// MODIFY CODE ONLY BELOW THIS LINE
// Map Supabase polygon list to library polygon list
return supabasePolygons?.map((polygon) {
// Get places for this polygon
final polygonPlaces = supabasePolygonPlaces
?.where((place) => place.polygonId == polygon.id)
.map((place) {
return supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema
.createPolygonPlaceStruct(
id: place.id,
title: place.title,
coordinates:
LatLng(place.latitude ?? 0.0, place.longitude ?? 0.0),
polygonId: place.polygonId,
order: place.order,
);
}).toList() ??
[];
return supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema.PolygonStruct(
id: polygon.id,
title: polygon.title,
zoom: polygon.zoom ?? 11.0, // Default zoom
strokeColor: polygon.strokeColor,
strokeOpacity: polygon.strokeOpacity,
fillOpacity: polygon.fillOpacity,
fillColor: polygon.fillColor,
strokeWeight: polygon.strokeWeight ?? 2,
polygonPlaces: polygonPlaces,
);
}).toList() ??
[];
/// MODIFY CODE ONLY ABOVE THIS LINE
}
**Supabase Places **mapping function
For mapping places I use toPlaceModel as the function name.
For the return value we are using the place (code-whims-place-manager) data type. Make sure to check Is List

For the arguments we are passing a list of rows from our place table.

Replace the default code with the code below
import 'dart:convert';
import 'dart:math' as math;
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:google_fonts/google_fonts.dart';
import 'package:intl/intl.dart';
import 'package:timeago/timeago.dart' as timeago;
import '/flutter_flow/custom_functions.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/lat_lng.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/place.dart';
import 'package:ff_commons/flutter_flow/uploaded_file.dart';
import '/backend/schema/structs/index.dart';
import '/backend/supabase/supabase.dart';
import "package:supabase_google_map_library_s065pd/backend/schema/structs/index.dart"
as supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema;
List<supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema.PlaceStruct> toPlaceModel(
List<PlaceRow>? supabasePlaces) {
/// MODIFY CODE ONLY BELOW THIS LINE
// map supabase place list to library place list
return supabasePlaces?.map((place) {
return supabase_google_map_library_s065pd_data_schema.createPlaceStruct(
title: place.title,
description: place.description,
latLng: LatLng(place.latitude ?? 0.0, place.longitude ?? 0.0),
imageUrl: place.imageUrl,
id: place.id,
);
}).toList() ??
[];
/// MODIFY CODE ONLY ABOVE THIS LINE
}
Query data from the database
Now we can query from the database, map the functions, and set the local page state variables.
First, select the Widget tree menu item. Next, click the top level widget. In my case the top level widget is HomePage.

Now go to the far right of the screen so that we can add actions

Here is a high level overview before we get started. This is just one way you can query your data.
I have one parallel action with three different action “branches”. You initially will start with two branches. Before getting started you can add the third branch by clicking Add Action on the right side.

On the first branch I’m querying the place table.
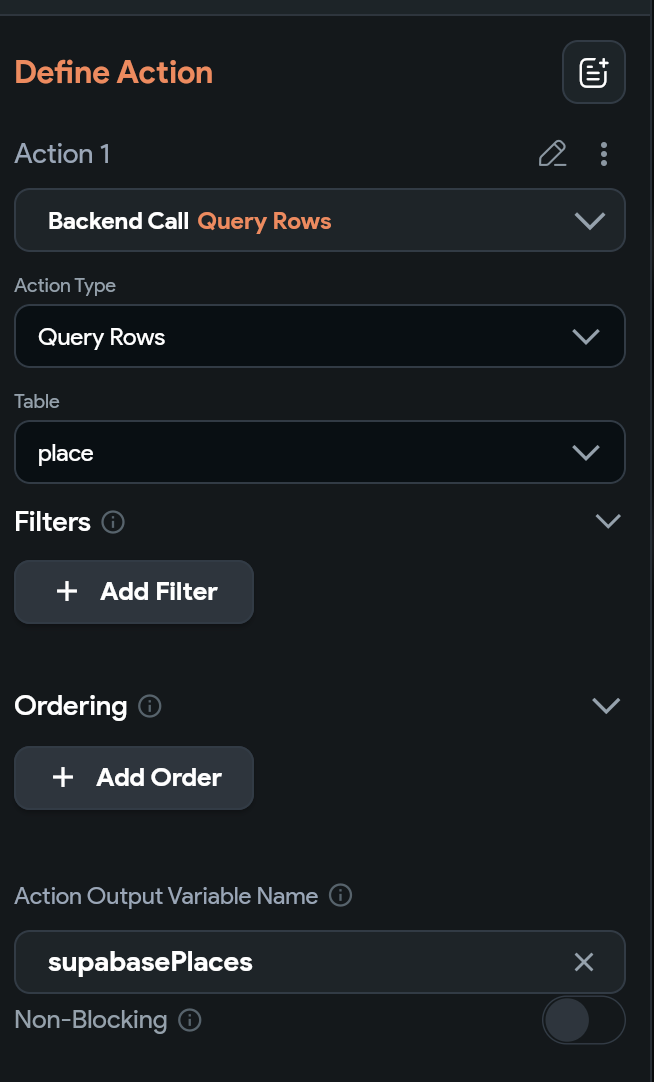
Note that I am setting the action output variable as supabasePlaces. Now click the plus button under this action to create another action. For action 2 we are updating our placeList page state.

When clicking Value to set, click Custom Functions, and choose the toPlaceModel custom function.

For the supabasePlaces argument click Action Outputs and choose supabasePlaces

Now we will do the same for polygon and polylines. The main difference is that we are first querying polygon/polylines and then we query the place tables for each.
Let’s start by querying polygons. Notice we have supabasePolygons as the action output variable

Create a new action under the polygon action to query polygonPlaces. I have name the action output variable for this supabasePolygonPlaces

Now let’s create another action to set the polygonList page state. Similar to places we will also choose **Custom Functions **and choose toPolygonPlaceModel.
Similar to what we did with places, choose Action Output Variables and use those as arguments for this function

Now let’s do the same for polylines.
Create an action to query the polyline table with action output variable supabasePolylines

Create an action to query the polyline_place table with action output variable supabasePolylinePlace

Now update the polylineList page state by choosing the custom action and passing the action output variables to that function

Pass the local page state variables to the map widgets
We can now set the local page state variables to the parameters of the map widgets


With data in your database you can now run the app and should see polygons, polylines, etc.

Final Thoughts
Lastly, with libraries, you now don’t have access to the source code without downloading the code
Instead you can generate the code for any widget including maps with custom markers, polylines, polygons, etc at https://codewhims.com/